
Get Started
Welcome to the Rogers Community Forums! Start your journey here.

Welcome to the Rogers Community Forums! Start your journey here.

Catapult yourself into a hub of endless viewing possibilities! A warm welcome to The Ignite Couch...

*Making sure these dates are accurate is our top priority. Sometimes things change beyond our...

Hello Community! With the start of the 2023 MLB season and the NHL and NBA Playoffs...
If your internet package includes unlimited usage, be sure to take advantage of the highest quality for your choice of video streaming services. Netflix For each Netflix account profile you can choose from Auto, Low, Medium or High...
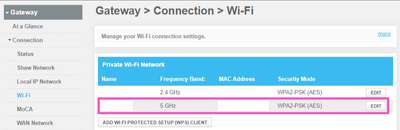
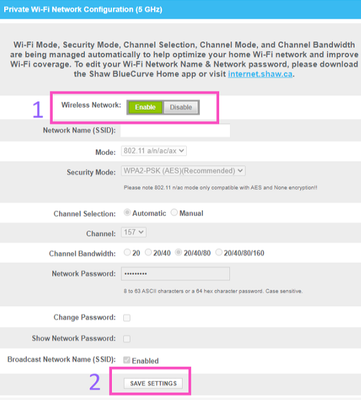
Hello Community, Many devices that are single band 2.4 GHz capable only, such as certain printers, home security, cameras, Internet of Things (IoT) devices will not connect to a network that is using band steering because of compatibility limitati...
How does Advanced Security help protect my data and devices? When enabled, Advanced Security in Ignite HomeConnect continuously monitors your home network to automatically block suspicious activity and inform you of potential security concerns...
To help keep your data and devices protected around the clock, Advanced Security monitors your home WiFi network for online threats in real time and alerts you of any suspicious activity. This feature is included with Ignite HomeConnectTM. Ther...
With the release of iOS 14, Apple introduced a new WiFi network privacy setting called Private Address to protect users from third parties attempting to track their behaviour on their iOS devices. This feature may require Rogers customers current...